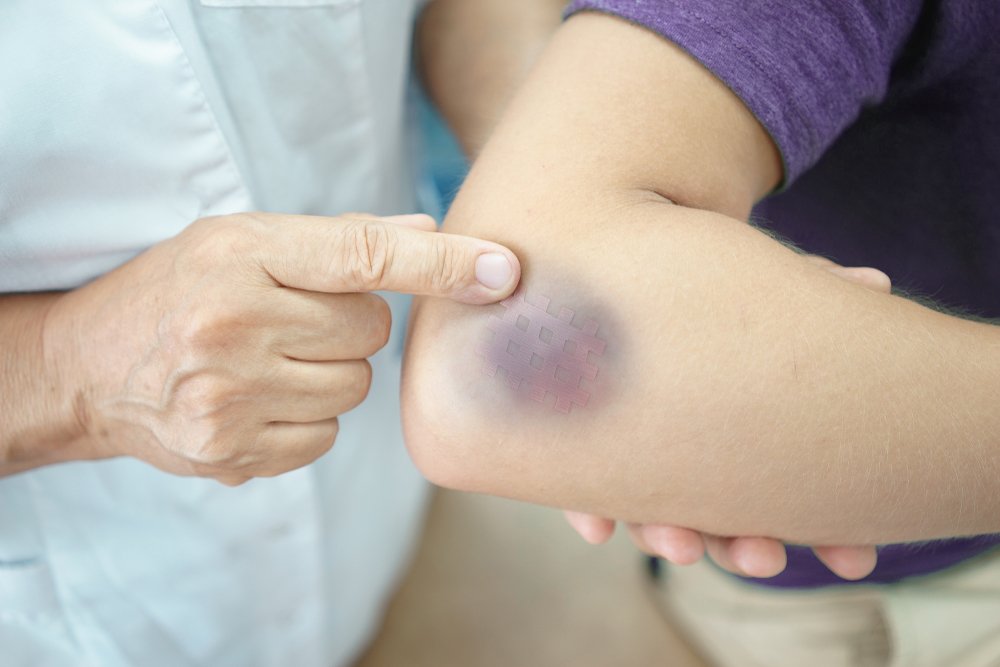
Bruises typically result from physical trauma such as falls or bumping into something; however, if you notice bruises forming frequently without an obvious trigger, there could be a health issue to address.
Lacking essential vitamins can contribute to easy bruising. This article will detail how you can protect yourself by eating healthily and taking any required supplements if necessary.
Vitamin C
People who bruise easily may not be receiving enough Vitamin C, K and B12. These essential vitamins play an essential role in maintaining the health of blood vessels and the skin; without sufficient levels, blood vessels become weaker and more prone to breakage or bleeding. Eating healthily through a varied diet including plenty of fruits and vegetables should help ensure adequate levels of these vitamins in your system to keep bruising at bay.
Vitamin C is essential in encouraging collagen formation, helping maintain strong skin, and thus helping prevent bruising. Meanwhile, vitamin K plays an essential role in blood clotting which further lowers risk. Any deficiencies of this nutrient could leave people more susceptible to bruises while hindering wound healing processes.
B12 is essential for DNA synthesis and serves as a cofactor in converting homocysteine to methionine, with insufficient B12 levels leading to hyperhomocysteinemia – an increase in homocysteine and methionine concentrations – as well as fatigue, forgetfulness, tingling hands or feet and other symptoms caused by B12 deficiency.
Vitamin deficiencies can usually be resolved with changes to diet and supplements; however, if symptoms of easy bruising are particularly prominent then vitamin infusion therapy may provide additional support and may improve its appearance. It has been found effective at alleviating this symptom.
Vitamin infusion therapy is an efficient and safe solution to improve the appearance of easy bruising. It may also be suitable for individuals who are at greater risk due to genetic predisposition or other health concerns; by targeting nutritional deficiencies through this therapy, patients can help avoid long-term complications like heart disease and depression. It’s best to discuss all options with healthcare providers to determine the appropriate course of action; they may even help address any underlying health conditions like anemia that contribute to this issue.
Vitamin K
Accidents happen, but frequent bruising could be indicative of underlying problems, including weak capillaries or thin skin that is susceptible to bruises, vitamin deficiency or an imbalanced diet that makes you susceptible. Dietary changes or supplementation could provide additional support. If this sounds familiar then seek medical advice as soon as possible! Vitamins C, K, B6 and Folate may all help ease bruising. A diet rich in citrus fruits, peppers and leafy green vegetables will increase these vitamins in your system; vitamin C works to boost collagen production while also acting as an antioxidant; Vitamin K aids blood clotting while speeding wound healing, while also supporting bone health by helping regulate calcium levels in bone tissue; it also aids the body absorb folic acid which is necessary for cell development.
Vitamin K deficiency can contribute to easy bruising as its lack weakens blood vessels, leading to leakage of blood under the skin that results in bruises. A low platelet count is another contributing factor as these blood cells help minimize bleeding; many health conditions, such as Von Willebrand disease or liver disease can reduce platelet count significantly.
Low iron levels can make bruising more likely. To combat this problem, increase your intake of foods rich in iron such as lean meats, fish and eggs. Or alternatively take iron supplements for enhanced health benefits and reduced bruising.
Vitamin deficiencies may contribute to easy bruising in older adults due to thinner blood vessels which become more likely to burst as people age. This increases their susceptibility for fractured artery walls rupturing under strain. Additionally, illnesses and treatments may contribute to easy bruising by distancing the balance of minerals in your body, so consulting a doctor about diet changes or supplements could reduce its occurrence. Folate, Vitamin B-9 and B-12 may also cause easy bruising as they are required for producing 5-methyltetrahydrofolate which plays an essential role in DNA methylation, purine/thymidine/myelin production as well as protein/neurotransmitters/fatty acid and phosphatidylcholine synthesis.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient, meaning the body cannot make its own supply and must obtain it from food or dietary supplements. This essential nutrient plays an integral part in maintaining normal function of blood vessels and red blood cell production, with low levels potentially making their vessels more fragile, making bruising more likely, fatigue setting in, weakness, indigestion shortness of breath or depression all symptoms that a low normal level might bring about.
If a person experiences unexplained bruising, it is vital to visit their physician and undergo testing in order to ascertain its cause. A physician can evaluate vitamin levels in your body and make suggestions regarding diet or supplementation as a means to ensure you’re getting enough essential nutrients in your daily intake.
Vitamins C, K and B12 may contribute to easily bruised tissues in the body by aiding with cartilage formation, blood vessel maintenance and muscle maintenance. A person who consumes an unhealthy diet or takes certain medications could be at increased risk of vitamin deficiencies that cause easy bruising.
Lack of these vitamins may contribute to frequent bruising by maintaining healthy and strong platelet cells in your blood, which clot broken vessels to stop bleeding. When platelet counts drop significantly, however, bruising becomes easier as your body finds it harder to stop bleeding when blood vessels rupture.
Vitamins C, K and B12 all play an essential role in normalizing the clotting process and keeping blood vessels near the surface protected from injury. If someone’s levels of these vitamins drop below adequate levels, their blood clots more slowly, leading to less protection of vulnerable blood vessels nearer to the skin surface. As such, low levels can increase chances of bruises.
Deficits in vitamins can be caused by many different conditions that afflict the liver, intestines and stomach, such as liver diseases or Von Willebrand disease inherited conditions like hemophilia or Von Willebrand disease that interfere with normal clotting processes such as hemophilia or Von Willebrand disease as well as Crohn’s disease or antibiotic medications that prevent the body from absorbing essential vitamins.
Folate
Bruises occur when blood vessels beneath the skin burst, releasing their contents onto the surface, which results in dark red or purple spots that eventually heal as your body absorbs back in any excess blood. Sometimes bruises are caused by vitamin deficiencies; therefore it is crucial that medical assistance be sought immediately for diagnosis and treatment of such conditions. Common culprits for easily bruised skin are iron, Vitamin C, Vitamin K and Vitamin B12. Low levels of these nutrients can cause capillaries under the skin to break easily, increasing your chances of bruising with minor bumps or trauma. Other possible causes for easy bruising could be von Willebrand disease or liver or kidney diseases that deplete proteins needed for blood clotting, like von Willebrand disease.
Common belief holds that pale skinned people are more prone to easy bruising. While this may be partially true, lighter complexioned people do tend to show discolorations more readily than would occur on darker skintones, making bruises more apparent on lighter complexions.
Folic acid (vitamin B12) is an essential nutrient necessary for maintaining healthy blood cells. A deficiency can result in anemia as it prevents your body from making normal red blood cells; or lead to megaloblastic anemia when bone marrow produces large, abnormal red blood cells.
Vitamin B12 deficiency can result from several conditions, such as gastroparesis and Crohn’s disease, pernicious anemia and some chronic illnesses like HIV. Other signs include fatigue, weakness, memory problems and depression – telltale indicators that vitamin B12 deficiency exists.
Bruising can be annoying and inconvenient, but it’s important to keep in mind that it is one way the body communicates something is off balance. A diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables may help avoid vitamin B12 deficiency; those at risk can get regular injections or supplement their intake daily with 1,000 to 2,000 micrograms through oral supplementation.