Does Light Therapy Really Work?
There are many claims about the effectiveness of light therapy. One claim is that it works well for depression and insomnia. Another claim is that it can help with skin conditions. While these may be true, there are also many who argue that it is unsafe. What is more, there are many adverse effects of light therapy that should be considered before undergoing treatment.
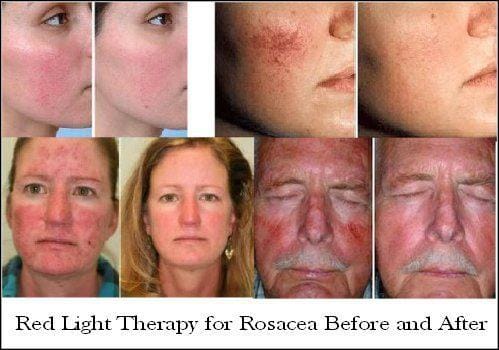
Red light therapy
Red light therapy is a new treatment that can help you heal faster. This is because the light has the ability to penetrate the skin. It can also improve collagen and elastin production, which helps your skin look younger.
The way the energy from red light interacts with your body is called photobiomodulation. The energy comes from the mitochondria in your cells. These cells are the powerhouses in your body. They create a lot of energy, and they can help your cells heal by producing nitric oxide, reactive oxygen species, and ATP. You can also benefit from increased blood flow, which means your endorphins will work harder to relieve pain.
Besides being able to reduce inflammation and repair damaged cells, red light therapy can also help you lose weight. This is because your skin will become more elastic. Also, you’ll get more sleep and less joint and muscle pain. Your skin will appear more youthful, and your hair will be healthier.
There are several types of red light therapy devices available, and they vary in intensity. Some can produce 800-900 nm of red light, while others use a wider spectrum of wavelengths. Wide-spectrum devices come with money-back guarantees, so you’ll know that your treatment is worth it.
Red light works to strengthen the mitochondria in your cells, which are responsible for storing energy and healing your body. When you have an injury or chronic pain, you’ll see improvement from the therapy. However, the results will depend on the amount of time and the amount of energy you’re getting. That’s why it’s important to find the right dosage.
If you are considering red light therapy, you’ll want to talk to a medical professional. This will ensure that you are able to safely and effectively use the device.
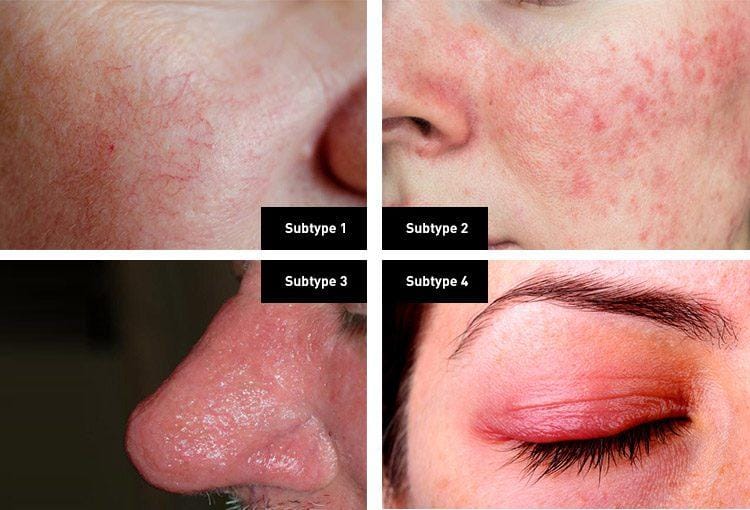
Red light therapy has been used to speed up wound recovery and improve collagen and elastin production. In addition, it has been used to treat rosacea, acne, and psoriasis. Even if you are not suffering from any of these conditions, you can still take advantage of this powerful therapeutic method.
In the last few years, the scientific community has taken an interest in red light therapy. Scientists are looking into its use as a drug-free, non-invasive treatment for nerve damage. And manufacturers are testing it for use in the nasal passage.
You can even buy at-home devices that produce the 630-700 nm of red light. Most of these devices are comfortable and do not emit heat. They also are effective, and have been proven by many peer-reviewed studies.
Red light therapy is a powerful therapeutic tool, and it can be used to treat just about any medical condition. While it does have some side effects, it is very safe and easy to use.
Effects on sleep
Light therapy, also known as phototherapy, is a treatment that is used to help people sleep better. It has been found to be effective in treating insomnia and other sleep problems. In addition, light therapy can be beneficial to those who suffer from depression.
Light therapy is a type of therapy that involves sitting in front of a light box. The box uses bright light to affect the brain chemicals that are linked to mood and the sleep-wake cycle. A small study has shown that this light can improve alertness and sleep quality.
Bright light therapy is helpful for patients with circadian rhythm sleep disorders such as nocturnal sleep apnea, advanced sleep phase disorder, and delayed sleep phase disorder. These types of sleep disorders cause people to wake up early and to experience difficulty falling asleep. During the morning, the bright light helps to re-set the internal clock, which may then result in more consolidated sleep at night.
In general, light therapy is safe and does not have significant negative side effects. However, there are several factors that may play a role in whether it is effective. For instance, the timing of the light, the intensity of the light, and the duration of the light may have a negative or positive effect on the quality of the sleep.
In order to evaluate the effectiveness of bright light therapy, scientists performed a pilot study. Participants were asked to take part in a four-week intervention. One group of individuals were exposed to a sham-controlled study while the other group was treated with bright light therapy. At the end of the study, participants were surveyed and given questionnaires to complete. Some questions were completed in the laboratory, while others were sent home with the participants.
Bright light therapy is not a substitute for other medical treatments. Ultimately, it is important to seek advice from your doctor about whether or not this type of treatment is right for you. Whether or not you decide to try light therapy, you should follow the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure your comfort.
Several studies have been conducted on the effect of light therapy on sleep. However, researchers have not yet fully understood the mechanism behind the effectiveness of the treatment. Until researchers understand the relationship between light and the circadian rhythm, it will be impossible to determine the exact benefits of bright light therapy.
Although the use of light is not without its risks, light therapy has been found to be effective in alleviating symptoms of insomnia and other sleep-related disorders. Researchers suggest that the light is most effective first thing in the morning, after a person has had a full night’s sleep. Because of this, light therapy should be finished one or two hours before bedtime.
Adverse side effects
Light therapy has been shown to be very effective for treatment of seasonal affective disorder (SAD) and other conditions. However, it has also been shown to cause adverse side effects. These effects are usually mild, although some users experience more serious reactions. Fortunately, the side effects are generally short-lived, but they can occur if light therapy is not used correctly.
One of the most common side effects associated with light therapy is eye strain. Fortunately, this can be easily managed by using a shorter-than-average session or moving farther away from the device. Some people may experience itchy or stinging skin, itchiness or rash, or even burning.
While these side effects are not considered serious, they should be reported to your doctor. In addition, if you have serious depression, you should ask your doctor about the appropriateness of light therapy. He or she will also be able to provide you with a recommendation.
Another possible side effect is an increased risk of developing skin cancer later in life. If you are concerned about this, you should contact your doctor, especially if your symptoms are getting worse. This is especially true for those who have had cancer in the past. Using a sunscreen or a UV blocking agent can help, but if you do not have it, you should avoid sunlight altogether.
Lastly, a study found that bright light therapy can cause a condition known as autonomic hyperactivity. Approximately 8.8% of patients experienced headaches, jumpiness or jitteriness. When light therapy was stopped, these symptoms returned in the same amount of time. A fifth study of patients with age-related macular degeneration showed that low-intensity light therapy could improve the vision of these patients.
As with any new medical procedure, light therapy should be evaluated carefully before it is administered to any patient. There are a number of contraindications to using it, including systemic lupus erythematosus, pregnancy, retinal diseases, and photosensitivity. Those who are pregnant, have a history of migraine, or suffer from bipolar disorders should consult their physician first.
Although the benefits of light therapy are numerous, the risks are significant. For example, in the case of age-related macular degeneration, exposure to ultraviolet light can lead to blindness, premature aging, and skin cancer.
Nonetheless, light therapy has been proven to be effective in treating SAD, and it has fewer negative side effects than previously thought. It is an ideal adjunct to antidepressant medication, but it must be used under the supervision of a doctor. You should also be aware that insurance reimbursement for this treatment is not as consistent as you might think. Moreover, you should be careful about overdoing it.
As for the actual results of using light therapy, the newest research shows that it can be very effective in treating nonseasonal depression. Symptoms usually clear up within a week.