Enhancing First Aid Techniques with the Chain of Survival
Imagine finding yourself in a situation where someone’s life is hanging by a thread. Every second counts, and the actions you take in those crucial moments could mean the difference between life and death. This is where first aid techniques come into play, serving as the vital link that bridges the gap between an emergency situation and professional medical assistance.
In this article, we will explore the concept of enhancing first aid techniques with the Chain of Survival – an innovative approach that can maximize survival rates in cardiac emergency situations. We will delve into each step of this chain, dissecting its significance and providing insights on how to execute it effectively. By understanding and implementing these techniques, you can be empowered to save lives when it matters most.
Get ready to embark on a journey that will equip you with invaluable knowledge and skills, enabling you to make a real difference in critical situations. From early recognition of cardiac arrest to rapid access to advanced medical care, we will guide you through each step of the Chain of Survival. By immersing yourself in this comprehensive exploration, you are taking a proactive step towards becoming a crucial link in saving lives.
So brace yourself for an enlightening experience as we dive into the depths of first aid techniques enhanced by the Chain of Survival. You will gain practical insights that transcend theory, leaving you better prepared for any emergency scenario that may arise. Together, let us embark on this journey towards making our world safer and more resilient.
The Importance of First Aid Techniques in Saving Lives
First aid techniques are not mere skills to be learned; they are powerful tools that have the potential to save lives in critical situations. When faced with an emergency, the ability to provide immediate assistance can make all the difference between life and death. First aid serves as a vital bridge between an incident occurring and professional medical help arriving.
By equipping individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to respond effectively in emergencies, first aid techniques empower ordinary people to become extraordinary heroes. Whether it is administering CPR during a cardiac arrest or stopping severe bleeding, these techniques buy valuable time until medical professionals can take over. Moreover, the confidence that comes from being trained in first aid allows individuals to step forward as responsible community members, capable of providing immediate support when it matters most.
 The Chain of Survival: A Powerful Tool in Cardiac Emergency Situations
The Chain of Survival: A Powerful Tool in Cardiac Emergency Situations
In the realm of first aid, time is of the essence when it comes to saving lives, especially in cardiac emergency situations. That’s where the Chain of Survival proves to be an invaluable tool. It is not merely a series of steps; rather, it is a well-coordinated sequence designed to maximize the chances of survival for someone experiencing cardiac arrest.
The Chain of Survival consists of several crucial links that work together seamlessly to improve outcomes during an emergency. Starting with early recognition, which involves promptly identifying signs and symptoms of cardiac arrest, this critical link sets everything into motion. By recognizing the problem early on and swiftly activating emergency medical services (EMS), precious minutes are saved.
Early Recognition of Cardiac Arrest
In the realm of first aid, the ability to swiftly recognize cardiac arrest is a paramount skill. Early recognition serves as the catalyst for initiating life-saving interventions, ensuring prompt medical attention and increasing the chances of favorable outcomes. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of cardiac arrest enables individuals to respond promptly and initiate appropriate measures, thereby potentially saving precious lives.
One crucial aspect of early recognition is being alert to the indicators that may precede cardiac arrest. These can include sudden loss of consciousness, absence of breathing or abnormal breathing patterns, and a lack of pulse. Vigilance in monitoring changes in an individual’s condition, especially during high-risk scenarios such as heart attacks or trauma situations, allows for swift identification of potential emergencies. By actively engaging our senses and staying attuned to the subtle cues presented by an individual in distress, we empower ourselves to be proactive first responders in critical moments.
Early Activation of Emergency Medical Services (EMS)
When faced with a medical emergency, time becomes an invaluable asset in the race against death. Engaging emergency medical services (EMS) at the earliest opportunity is crucial to maximizing the chances of survival. Through prompt activation of EMS, individuals can swiftly access professional assistance and ensure a coordinated response that optimizes patient outcomes.
By activating EMS immediately, precious minutes are saved in initiating critical life-saving interventions. Trained dispatchers provide essential guidance over the phone, offering step-by-step instructions for first responders while help is on its way. This early activation not only expedites the arrival of medical professionals but also triggers a well-orchestrated chain reaction that mobilizes resources and expertise necessary for efficient pre-hospital care.
Understanding the significance of early EMS activation empowers individuals to take immediate action when confronted with emergencies, bridging the gap between initial response and comprehensive medical attention. By doing so, we can ensure that no precious seconds are wasted in bringing expert assistance to those in need, ultimately saving lives.
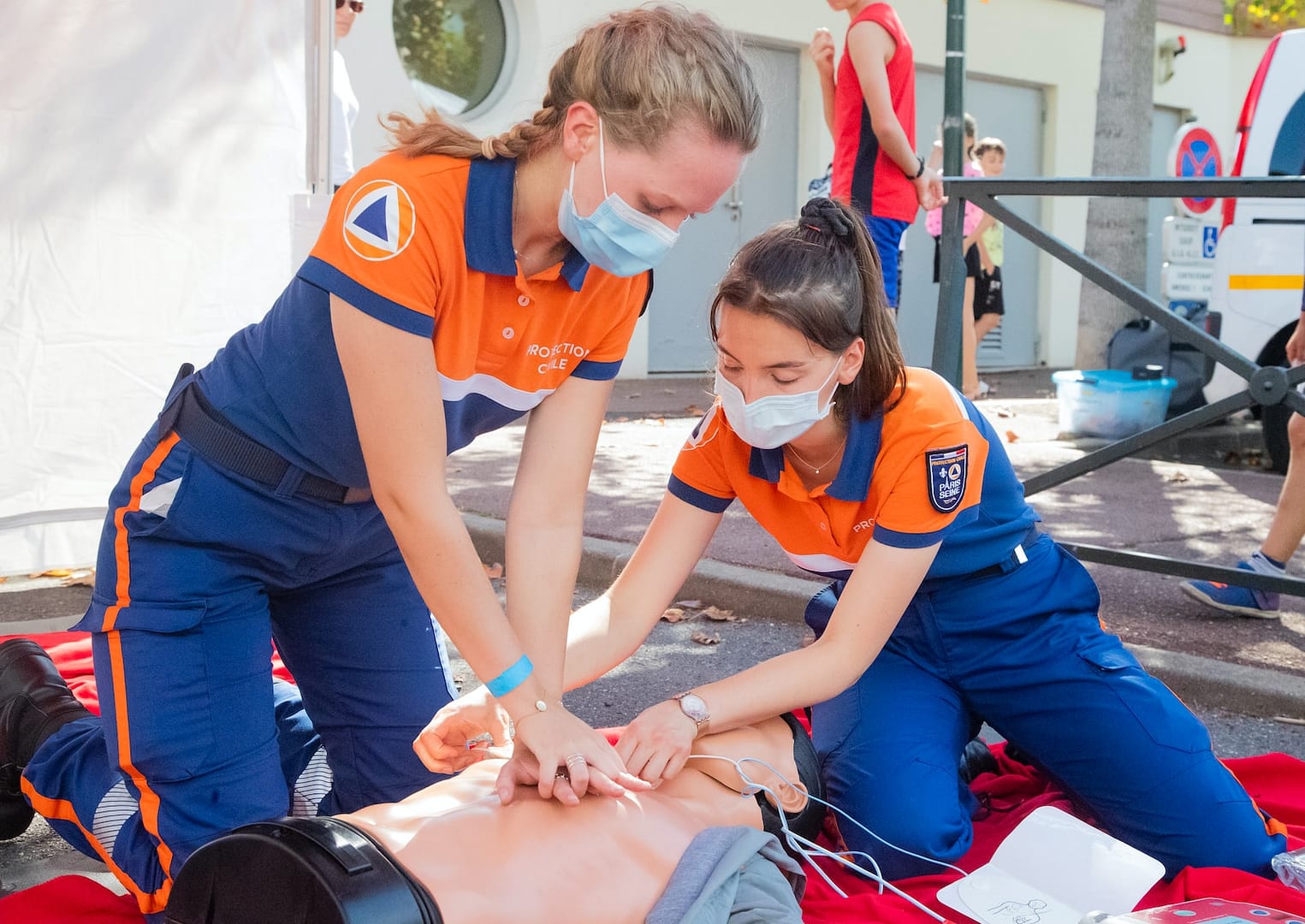
High-Quality Chest Compressions
When it comes to providing life-saving assistance during a cardiac emergency, the significance of administering high-quality chest compressions cannot be overstated. Chest compressions form the cornerstone of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), ensuring continuous blood flow to vital organs and increasing the chances of survival. To perform effective chest compressions, one must first position themselves correctly. Placing the heel of one hand on the lower half of the victim’s sternum, followed by interlacing fingers and keeping arms straight, allows for optimal force distribution.
The depth and rate of compressions are crucial factors to consider. For adults, compressing with a depth of at least two inches but not exceeding 2.4 inches is recommended. Additionally, maintaining a compression rate between 100-120 compressions per minute ensures adequate blood circulation. It is essential to allow for full chest recoil after each compression, enabling optimal blood return to the heart and enhancing overall efficacy.
Early Defibrillation
In the chain of survival, early defibrillation plays a vital role in increasing the chances of survival for individuals experiencing cardiac arrest. Defibrillation is the process of delivering an electrical shock to the heart to restore its normal rhythm.
When a person’s heart goes into a state of ventricular fibrillation, where it quivers instead of beating effectively, immediate action is required. Early defibrillation with an automated external defibrillator (AED) significantly improves the chances of restoring the heart’s natural rhythm and saving the individual’s life.
The AED is a portable device that analyzes the heart rhythm and delivers an electric shock if necessary. It provides clear, user-friendly instructions that guide even untrained individuals in performing defibrillation effectively. The promptness with which defibrillation is initiated greatly impacts survivability, emphasizing the importance of having AEDs readily accessible in public places and training individuals on their usage.
Effective Airway Management
When faced with a cardiac emergency, ensuring effective airway management is crucial in maintaining oxygenation and facilitating resuscitation efforts. Promptly establishing and maintaining an open airway is vital for the successful delivery of oxygen to the lungs and subsequent circulation to the rest of the body.
In cases of cardiac arrest, the airway may become compromised due to factors such as loss of consciousness, tongue obstruction, or respiratory distress. First responders trained in effective airway management techniques can swiftly intervene to clear any obstructions and secure a patent airway. This allows for the administration of rescue breaths during cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), enabling oxygenation to resume and increasing the chances of restoring a stable rhythm.
The gold standard for airway management during CPR is endotracheal intubation, wherein a tube is inserted into the trachea to maintain an open passage for ventilation. However, this technique requires advanced training and expertise. In situations where endotracheal intubation cannot be performed promptly, alternative methods such as bag-mask ventilation or supraglottic devices like the laryngeal mask airway can be employed effectively.
It is imperative that individuals trained in first aid techniques understand how to assess and manage an obstructed or compromised airway efficiently. By mastering these skills, they can contribute significantly to improving patient outcomes by ensuring adequate oxygen delivery throughout resuscitation efforts.
Rapid Access to Advanced Medical Care
When a cardiac emergency occurs, time is of the essence. The prompt arrival of advanced medical care can significantly increase the chances of survival. Rapid access to specialized medical facilities equipped with advanced life support systems is a crucial link in the chain of survival.
Emergency Medical Services (EMS) play a vital role in facilitating rapid access to advanced medical care. Trained paramedics and emergency medical technicians are skilled in providing immediate assessment and stabilization, ensuring that patients receive appropriate care from the moment they arrive on scene. These dedicated professionals swiftly initiate necessary interventions, such as intravenous drug administration and advanced airway management techniques, while preparing patients for transportation to healthcare facilities capable of delivering specialized cardiac care.
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is the cornerstone of the Chain of Survival, a critical technique that can mean the difference between life and death in cardiac arrest situations. CPR combines chest compressions and rescue breaths to restore blood circulation and oxygenation in a person whose heart has stopped beating or is not effectively pumping blood. By performing CPR, bystanders can buy precious time until advanced medical help arrives.
During CPR, rescuers place their hands on the center of the victim’s chest and apply rhythmic compressions to mimic the pumping action of the heart. This helps maintain blood flow to vital organs, such as the brain. Additionally, rescue breaths are administered to supply oxygen to the victim’s lungs and bloodstream. Proper technique, including adequate depth and rate of compressions along with effective rescue breaths, is crucial for successful CPR.
Automated External Defibrillator (AED)
An Automated External Defibrillator (AED) is a vital tool in the Chain of Survival, designed to deliver an electric shock to the heart in cases of sudden cardiac arrest. This portable device plays a pivotal role in improving survival rates and ensuring effective first aid response. The AED’s user-friendly interface, coupled with its ability to analyze heart rhythms and provide clear instructions, empowers even non-medical professionals to confidently administer life-saving treatment.
When someone experiences sudden cardiac arrest, time is of the essence. By quickly attaching the AED’s electrode pads onto the victim’s bare chest, this smart device can assess the heart rhythm and determine if an electric shock is necessary. The AED then delivers a controlled shock to restore normal heart rhythm, increasing the chances of survival significantly. Its accurate analysis and immediate intervention make it an invaluable asset for bystanders and first responders alike.
Post-Cardiac Arrest Care
Once a patient has been successfully resuscitated following a cardiac arrest, the importance of post-cardiac arrest care cannot be overstated. This critical phase aims to stabilize the patient, prevent further complications, and enhance overall outcomes.
In this stage, healthcare professionals focus on several key aspects. Firstly, maintaining optimal oxygenation and ventilation is crucial for the patient’s brain function and organ perfusion. Adequate oxygen levels help minimize any potential neurological damage that may have occurred during the cardiac arrest event.
Next, therapeutic hypothermia or targeted temperature management (TTM) is often employed to protect the brain from further injury and improve survival rates. By carefully controlling the patient’s body temperature within a specific range, physicians can mitigate inflammation and reduce the risk of secondary brain damage.
To ensure comprehensive care, close monitoring of vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation is essential during this phase. In addition to physical observations, medical teams also assess neurological function using specialized tests to gauge cognitive recovery potential.
Finally, psychological support plays an integral role in post-cardiac arrest care. Patients often experience emotional distress and anxiety following such a traumatic event. By providing compassionate counseling and guidance to both patients and their families, healthcare providers can alleviate distress and foster hope for a brighter future.
Basic Life Support (BLS)
Basic Life Support (BLS) forms the foundation of emergency medical care, encompassing essential life-saving techniques that can be administered by anyone, irrespective of their medical background. BLS serves as a vital link in the Chain of Survival, enabling individuals to intervene promptly and effectively during critical situations.
In BLS, emphasis is placed on four primary components: early recognition of an emergency, activation of EMS, initiation of chest compressions, and provision of rescue breaths. These fundamental steps aim to maintain blood flow and oxygenation until professional medical help arrives. BLS training equips individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to address cardiac arrest, choking incidents, severe bleeding, and other life-threatening emergencies.
By learning BLS techniques such as proper hand placement for chest compressions and correct mouth-to-mouth resuscitation methods, individuals can become empowered first responders who possess the ability to make a significant difference in someone’s life. The accessibility and simplicity of BLS training encourage widespread participation in this crucial aspect of first aid. By fostering a culture where BLS becomes a common skill among community members, we create resilient networks ready to mitigate emergencies swiftly and effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Chain of Survival serves as a guiding light in the realm of first aid techniques, empowering individuals to take swift and effective action during cardiac emergencies. By recognizing the importance of early recognition, activation of emergency medical services, high-quality chest compressions, early defibrillation, effective airway management, rapid access to advanced medical care, and comprehensive post-cardiac arrest care, we can significantly enhance our chances of saving lives. With each link in this chain firmly established and diligently executed, we pave the way for a safer future where more lives can be preserved. Together, let us continue to strengthen our knowledge and skills in first aid techniques to become formidable guardians of life’s most precious gift.
Empowering Individuals to Save Lives with the Chain of Survival
In a world full of uncertainties, equipping individuals with the knowledge and skills to respond effectively in emergency situations is paramount. The Chain of Survival serves as a powerful tool in enhancing first aid techniques, enabling ordinary people to become extraordinary lifesavers. By understanding and implementing each link in the chain, individuals can confidently intervene during cardiac emergencies, potentially saving precious lives.
The first link in the chain is early recognition of cardiac arrest. By being aware of the signs and symptoms, individuals can swiftly identify when someone’s life hangs in the balance. This knowledge empowers them to take immediate action by activating emergency medical services (EMS), thus setting into motion a series of events that maximize the chances of survival. With each subsequent link – from high-quality chest compressions and early defibrillation to effective airway management and rapid access to advanced medical care – ordinary individuals become heroes, breathing life back into despairing moments.
Strengthening First Aid Techniques for a Safer Future
As society progresses and new advancements emerge, it is crucial that we adapt and strengthen our first aid techniques to ensure a safer future for all. One key aspect of enhancing first aid is continuous education and training. By remaining updated on the latest guidelines and protocols, individuals can sharpen their skills, allowing them to respond effectively to emergencies with confidence.
Moreover, creating awareness about the importance of first aid in the community plays a pivotal role in strengthening techniques. By encouraging people of all ages to undergo basic first aid training, we empower them to become active participants in emergency response situations. This not only increases the likelihood of saving lives but also fosters a sense of unity and responsibility within communities.