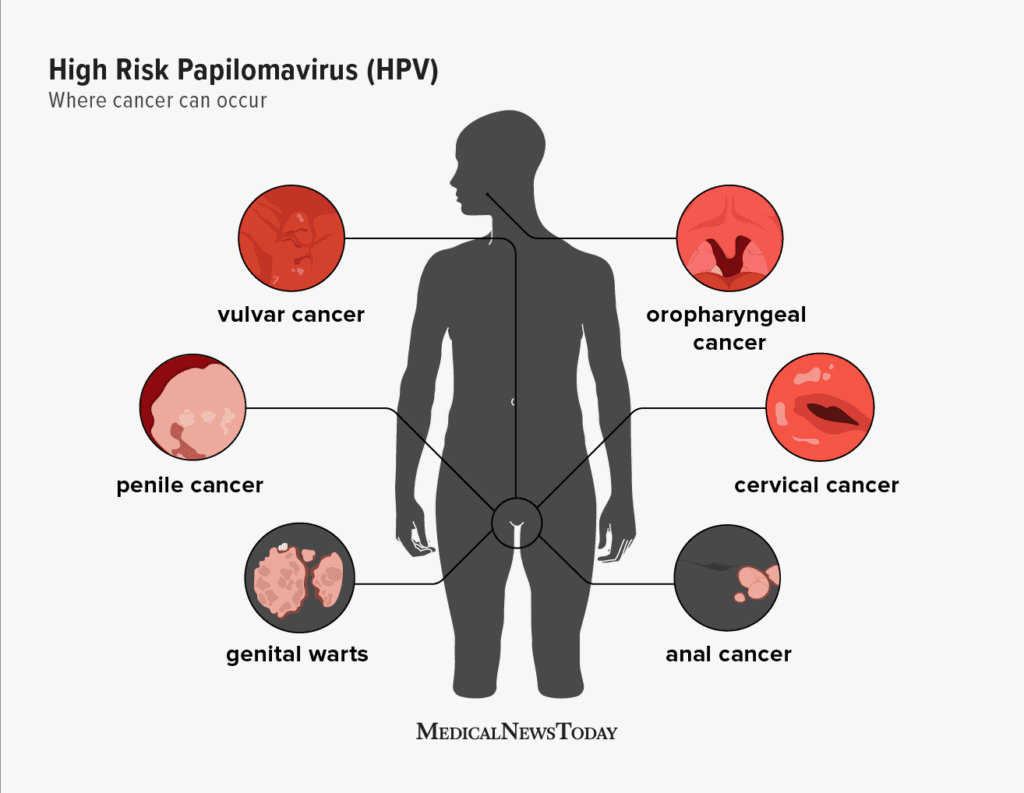
HPV, or the human papilloma virus, is a common sexually transmitted disease that can affect both men and women. It can be transmitted during vaginal sex, oral sex, or skin-to-skin contact. HPV doesn’t cause any symptoms in most people, but it can cause cancer if not treated. It is particularly dangerous for men, as it can lead to cancer in the throat and penis.
In the United States, HPV infection results in approximately 46143 cancers each year. Of those, almost twenty-five percent of penis cancers are caused by HPV. The most common type of HPV-related cancer is oropharyngeal cancer, which affects the throat, tonsils, and base of the tongue. There are many ways to get infected with HPV, and the body can respond differently to the same strain at different times.
There are several methods for detecting HPV in men. One method involves swabbing the penis with acetic acid or Lugol’s solution. This method, however, has very low sensitivity and specificity. This is because it is difficult to get a good cell sample from the penis skin. It is also difficult to detect HPV in men because most men won’t show any symptoms.
If a man has been partnered with an HPV-infected woman for a long period of time, there’s a chance that he’ll have the HPV virus. In most cases, HPV does not cause any symptoms and will clear up on its own within two years. If a man is concerned, he should consult a doctor.