uti symptoms female
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are a common health issue that can affect both men and women. However, females are more prone to developing UTIs due to anatomical differences. Understanding the symptoms of UTIs in females is crucial for early detection and prompt treatment.
Overview of UTI (Urinary Tract Infection) and its prevalence in females
A UTI occurs when bacteria enter the urinary tract, which includes the bladder, urethra, ureters, and kidneys. In females, the urethra is shorter and closer to the anus, making it easier for bacteria to travel up into the urinary tract.
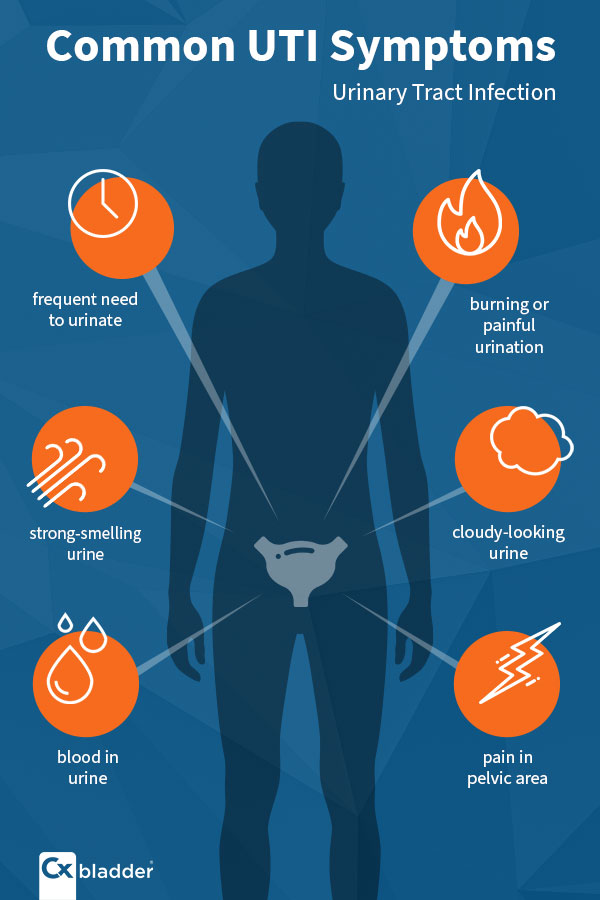
Common symptoms of UTIs in females include:
- Frequent urination: Feeling the need to urinate more often than usual.
- Burning sensation: Pain or a burning sensation during urination.
- Cloudy or bloody urine: Urine may appear cloudy or have a reddish tint.
- Strong-smelling urine: Urine may have a strong, unpleasant odor.
- Pelvic pain: Discomfort or pressure in the lower abdomen or pelvic area.
If left untreated, UTIs can lead to more serious complications, such as kidney infections. It is important for females experiencing these symptoms to seek medical attention promptly.
To prevent UTIs, it is recommended to drink plenty of water, urinate before and after sexual activity, practice good hygiene, and avoid holding urine for long periods.
In conclusion, understanding the symptoms of UTIs in females is crucial for early detection and timely treatment. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management.
What is a UTI?
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common infection that occurs in the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. It is more common in women than in men, with about 50% of women experiencing at least one UTI in their lifetime.
Explanation of UTI and its causes
UTIs are typically caused by bacteria entering the urethra and traveling up into the bladder. The most common bacteria responsible for UTIs is Escherichia coli (E. coli), which normally resides in the intestines but can cause an infection when it enters the urinary tract.
The symptoms of a UTI can vary but often include:
- Frequent urination
- Pain or burning sensation during urination
- Urgency to urinate
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Lower abdominal pain or discomfort
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Fatigue or malaise
If left untreated, a UTI can progress to a more severe infection and potentially spread to the kidneys, leading to more serious complications.
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a UTI. A healthcare professional can diagnose a UTI through a urine sample and prescribe appropriate antibiotics to treat the infection.
To prevent UTIs, it is recommended to drink plenty of water, urinate frequently, wipe from front to back after using the toilet, and avoid holding urine for long periods of time.
Common UTI Symptoms in Females
Frequent urination, burning sensation, and other symptoms
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are a common health issue that affects many women. Understanding the symptoms can help in early detection and prompt treatment. Here are some common UTI symptoms in females:
- Frequent Urination: If you find yourself needing to urinate more often than usual, it could be a sign of a UTI. This symptom is often accompanied by only passing small amounts of urine each time.
- Burning Sensation: A burning sensation or pain during urination is another typical symptom of a UTI. It can be quite uncomfortable and may indicate an infection in the urinary tract.
- Cloudy or Bloody Urine: UTIs can cause changes in the appearance of urine. If you notice that your urine is cloudy, has a strong odor, or contains blood, it could be a sign of an infection.
- Lower Abdominal Pain: Some women experience lower abdominal pain or discomfort when they have a UTI. This pain may be mild or severe and can persist even after urinating.
- Feeling Fatigued or Weak: In some cases, a UTI can cause fatigue or weakness. If you feel unusually tired or lacking energy, it’s worth considering whether a UTI could be the cause.
It’s important to note that not all women experience the same symptoms, and some may have no symptoms at all. If you suspect you have a UTI, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Risk Factors for UTIs in Females
Factors that increase the likelihood of developing UTIs
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common infections that affect millions of women each year. While anyone can develop a UTI, females are more prone to these infections due to certain risk factors. Here are some key factors that increase the likelihood of developing UTIs in females:
- Anatomy: The female anatomy makes it easier for bacteria to enter the urinary tract. The urethra, which is shorter in females, is located close to the anus, allowing bacteria from the intestinal area to easily reach the urinary tract.
- Sexual activity: Sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract, increasing the risk of UTIs. This is especially true for women who are sexually active or have a new sexual partner.
- Menopause: After menopause, a decrease in estrogen levels can lead to changes in the urinary tract, making it more susceptible to infections.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can affect the urinary tract, increasing the risk of UTIs.
- Urinary tract abnormalities: Structural abnormalities in the urinary tract, such as kidney stones or vesicoureteral reflux, can make it easier for bacteria to grow and cause infections.
- Urinary catheter use: The use of urinary catheters, especially long-term catheters, increases the risk of UTIs.
It is important for females to be aware of these risk factors and take preventive measures to reduce their chances of developing UTIs. This may include practicing good hygiene, staying hydrated, urinating before and after sexual activity, and seeking prompt medical attention if symptoms of a UTI arise.
Prevention and Home Remedies for UTIs
Tips to prevent UTIs and natural remedies for relief
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) can be uncomfortable and disruptive to daily life, especially for females. It is important to take preventive measures and seek relief when symptoms arise.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Urinate regularly: Emptying the bladder frequently can help prevent bacteria from multiplying.
- Wipe front to back: After using the toilet, always wipe from front to back to avoid spreading bacteria from the anus to the urethra.
- Avoid irritating products: Harsh soaps, douches, and feminine hygiene sprays can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the urinary tract.
- Wear breathable underwear: Cotton underwear allows for better airflow, reducing moisture and preventing bacterial growth.
- Cranberry juice or supplements: Consuming cranberry juice or taking cranberry supplements may help prevent UTIs by inhibiting bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract walls.
- Probiotics: Probiotic supplements or foods like yogurt can promote a healthy balance of bacteria in the urinary tract.
- Warm compress: Applying a warm compress to the lower abdomen can help alleviate discomfort caused by a UTI.
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can provide temporary relief from UTI symptoms such as pain and inflammation.
It is important to note that while these home remedies may provide relief, they are not a substitute for medical treatment. If symptoms persist or worsen, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
When to Seek Medical Attention for UTI Symptoms
Indications that medical intervention is necessary
If you are experiencing symptoms of a urinary tract infection (UTI), it is important to know when to seek medical attention. While some mild UTIs may resolve on their own, certain indications suggest the need for medical intervention.
- Severe pain or discomfort: If you are experiencing intense pain or discomfort in your lower abdomen, back, or pelvic region, it could be a sign of a more serious UTI or a complication such as a kidney infection.
- Blood in urine: The presence of blood in your urine, even if it is just a small amount, should not be ignored. It could indicate a more severe infection or an underlying condition that requires medical attention.
- Fever and chills: If you have a high fever (above 101°F) accompanied by chills, it may indicate that the infection has spread to your kidneys. This can be a serious condition and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
- Recurrent UTIs: If you have had multiple UTIs within a short period of time, it is important to seek medical attention. Recurrent UTIs may require further investigation to identify any underlying causes and prevent future infections.
- Urinary symptoms in pregnancy: Pregnant women with UTI symptoms should always seek medical attention. Untreated UTIs during pregnancy can lead to complications and potentially harm both the mother and the baby.
Remember, if you are unsure whether your symptoms warrant medical attention, it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide proper guidance and treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment of UTIs in Females
Medical tests and treatment options for UTIs
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common in females and can cause discomfort and pain. It is important to recognize the symptoms and seek medical attention for diagnosis and treatment. Here are some key points to consider:
- Symptoms: Common symptoms of a UTI in females include a frequent urge to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, pelvic pain, and lower abdominal discomfort.
- Medical Tests: To diagnose a UTI, a healthcare professional may ask for a urine sample to test for the presence of bacteria. This can be done through a urinalysis or urine culture. These tests help identify the specific bacteria causing the infection and determine the most effective treatment.
- Treatment Options: The primary treatment for UTIs in females is a course of antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare professional. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve before completion. Drinking plenty of water and urinating frequently can also help flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Prevention: To prevent UTIs, it is recommended to drink plenty of water, urinate before and after sexual activity, and practice good hygiene by wiping from front to back after using the toilet.
If symptoms persist or worsen despite treatment, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and management.
Recurrent UTIs in Females
Causes and management of recurrent UTIs
Recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) can be a frustrating and uncomfortable experience for many females. Understanding the causes and finding effective management strategies are crucial for preventing future infections.
The most common cause of recurrent UTIs in females is bacteria entering the urethra and traveling up to the bladder. This can happen due to various factors, including improper wiping technique, sexual activity, hormonal changes, or underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or kidney stones.
To manage recurrent UTIs, it is important to take preventive measures:
- Hygiene: Maintaining good hygiene practices, such as wiping from front to back after using the toilet, can help prevent the spread of bacteria.
- Urinate frequently: Emptying the bladder regularly helps flush out any bacteria that may have entered the urinary tract.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps dilute urine and flush out bacteria.
- Cranberry products: Some studies suggest that cranberry products may help prevent UTIs by preventing bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract walls.
- Antibiotics: In some cases, doctors may prescribe low-dose antibiotics to be taken regularly to prevent recurrent UTIs.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment options if you experience recurrent UTIs. They can provide guidance on identifying underlying causes and developing an effective management plan to reduce the frequency of infections.
Conclusion
Summary of key points and importance of early detection and treatment
In conclusion, it is crucial for females to be aware of the symptoms of urinary tract infections (UTIs) and seek early detection and treatment. Some common symptoms include frequent urination, a burning sensation during urination, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pelvic pain. It is important to note that not all UTIs present with symptoms, so regular check-ups are recommended.
Early detection and treatment are essential to prevent the infection from spreading to the kidneys, which can lead to more serious complications. UTIs are typically caused by bacteria entering the urethra and traveling up to the bladder. Maintaining good hygiene practices, such as wiping from front to back after using the restroom, staying hydrated, and urinating before and after sexual activity, can help reduce the risk of developing a UTI.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions) about UTI symptoms in females
Q: What are some common symptoms of a UTI in females?
A: Common symptoms include frequent urination, a burning sensation during urination, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pelvic pain.
Q: Can UTIs occur without any symptoms?
A: Yes, it is possible for UTIs to occur without presenting any noticeable symptoms. Regular check-ups are important for early detection.
Q: How can I prevent UTIs?A: Maintaining good hygiene practices, such as wiping from front to back after using the restroom, staying hydrated, and urinating before and after sexual activity, can help reduce the risk of developing a UTI.
Q: When should I seek medical attention for a suspected UTI?A: It is recommended to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or worsening symptoms, as prompt treatment is important to prevent complications.