There are many erectile dysfunction foods you can consume. You may even be surprised to learn that they may help you have a better erection! Listed below are some of the best foods for erectile dysfunction. Eat these foods regularly to enjoy a better erection and feel great! Also, remember to choose the ones that are healthy for your body and not just for your penis! Here are some of the best foods for erectile dysfunction you can eat and drink.
Fish, nuts, and eggs are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids are excellent for your heart and circulation and can help you achieve an erection. Other foods high in omega-3 fatty acids include walnuts, avocados, and fish. Several studies have also linked processed foods to depression, a common cause of erectile dysfunction. Fried food is another problem for men with erectile dysfunction. Fryers and fried foods can clog arteries and make it difficult to achieve an erection.
Flavonoids may help lower your risk for erectile dysfunction. Dark chocolate, cocoa powder, and green tea are a few of the many foods that contain flavonoids. Citrus fruits and vegetables are also rich sources of flavonoids. Studies have shown that these antioxidants can improve endothelial function and help men achieve erections. And if you have a folic acid deficiency, you should consider a diet rich in folic acid.
Donghai Deng owns a large restaurant in Shanghai and knows something about erectile dysfunction. Although he’s eloquent, he didn’t know how to explain the condition himself. So, he asked his father for advice. This man is famous for having a hard time conceiving and achieving an erection. The rest of the family members didn’t want to make the situation worse.
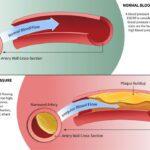
Many factors can cause erectile dysfunction, including diabetes, high blood pressure, and obesity. A heart problem reduces blood flow to the penis, which prevents optimal erections. A heart-healthy diet can also help prevent ED as certain vitamins and amino acids have been proven to help increase blood flow to the penis and improve erectile strength. But what about foods that don’t cause erectile dysfunction?
Another interesting study found an association between healthy diet and incident erectile dysfunction. Men who adhered to either the Mediterranean diet or the AHEI-2010 diet had the least incidence of the condition. The inverse association was most pronounced among men under 60 years of age. In all age groups, men who scored the highest on either dietary index had the lowest risk.
If you’re looking for a natural cure for erectile dysfunction, try these food remedies!