ADD, attention deficit disorder, is a condition that can affect children, and it may also cause problems in adulthood. It is a condition that involves difficulties with attention, memory, and impulsivity. It can cause learning and behavioural problems, and can coexist with other mental health disorders. It is usually diagnosed in childhood. It is a protected disability, meaning that institutions that receive federal funding cannot discriminate against individuals with ADHD.
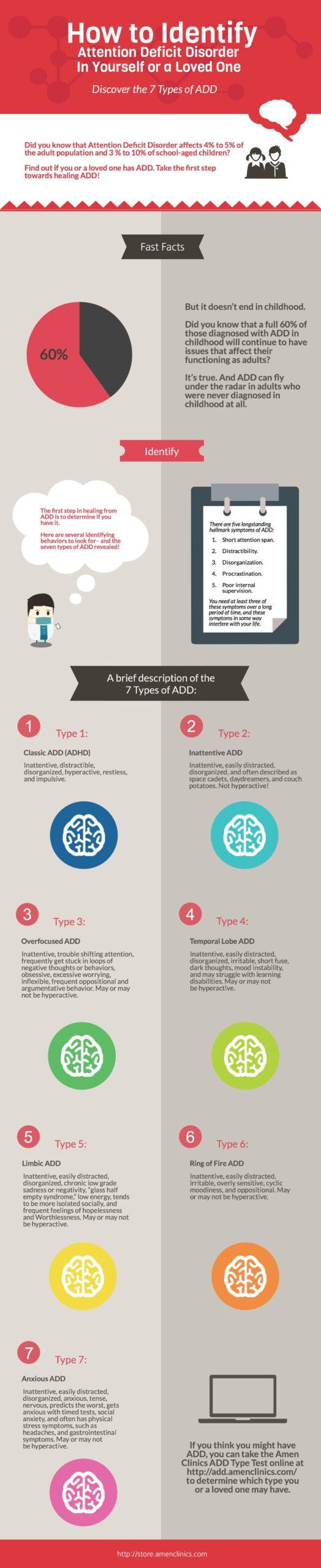
There are several different types of ADD. Among these are classic ADD, inattentive ADD, and hyperactive-impulsive ADD. Symptoms of each type of ADD can vary, but they generally have common characteristics. ADD is a brain disorder that is triggered by the production of neurotransmitters, such as dopamine. When dopamine is deficient, the person will experience inattentiveness.
Some research shows that the frontal lobes of the brain are affected in people with ADHD. This region is involved with the processing of visual information and emotions. In addition to these regions, the temporal lobes are also involved. These areas are responsible for visual processing, memory, and mood stability.
Various non-genetic factors have been linked to ADHD, including exposure to toxins. Low birth weight and premature birth have also been associated with the disorder. It is important to perform a thorough psychiatric evaluation before making any diagnosis.
The most common form of ADD is a combined form. This form of ADD has six or more symptoms of inattention and/or hyperactivity. Typical symptoms of this form of ADD include difficulty paying attention, being distracted, talking too much, and impulsive behavior. Medications can help reduce hyperactivity, but they can also make some people with ADHD worse. The goal of treatment is to improve the child’s ability to function at school and at home. Behavioral therapy is often used, as well as medication intervention. Parents can make treatment decisions themselves, but they may need assistance from a health care provider.
There are many different treatments for ADD, and the best one for your child depends on the type. Some children will respond well to a combination of behavior therapy and stimulant medications. They will also benefit from family and group therapy, and from support groups. For adults with ADD, cognitive behavioral therapy is a good option. A therapist can also provide emotional healing.
There are many non-genetic causes of ADHD, such as extreme stress during pregnancy, early exposure to toxins, and premature birth. A doctor can help you determine the cause of your child’s ADD and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
There are several non-invasive brain imaging techniques that can be used to study the brain activity of a child with ADD. These tests use SPECT scans to measure blood flow to the brain. Amen uses these scans to study both classic and inattentive ADD. He also studies the condition called Anxious ADD. Anxious ADD is characterized by inattentiveness, fearfulness, and difficulty focusing. The main difference between Anxious ADD and classic ADD is that Anxious ADD is more likely to involve physical stress symptoms such as headaches.